Section: New Results
time decoding
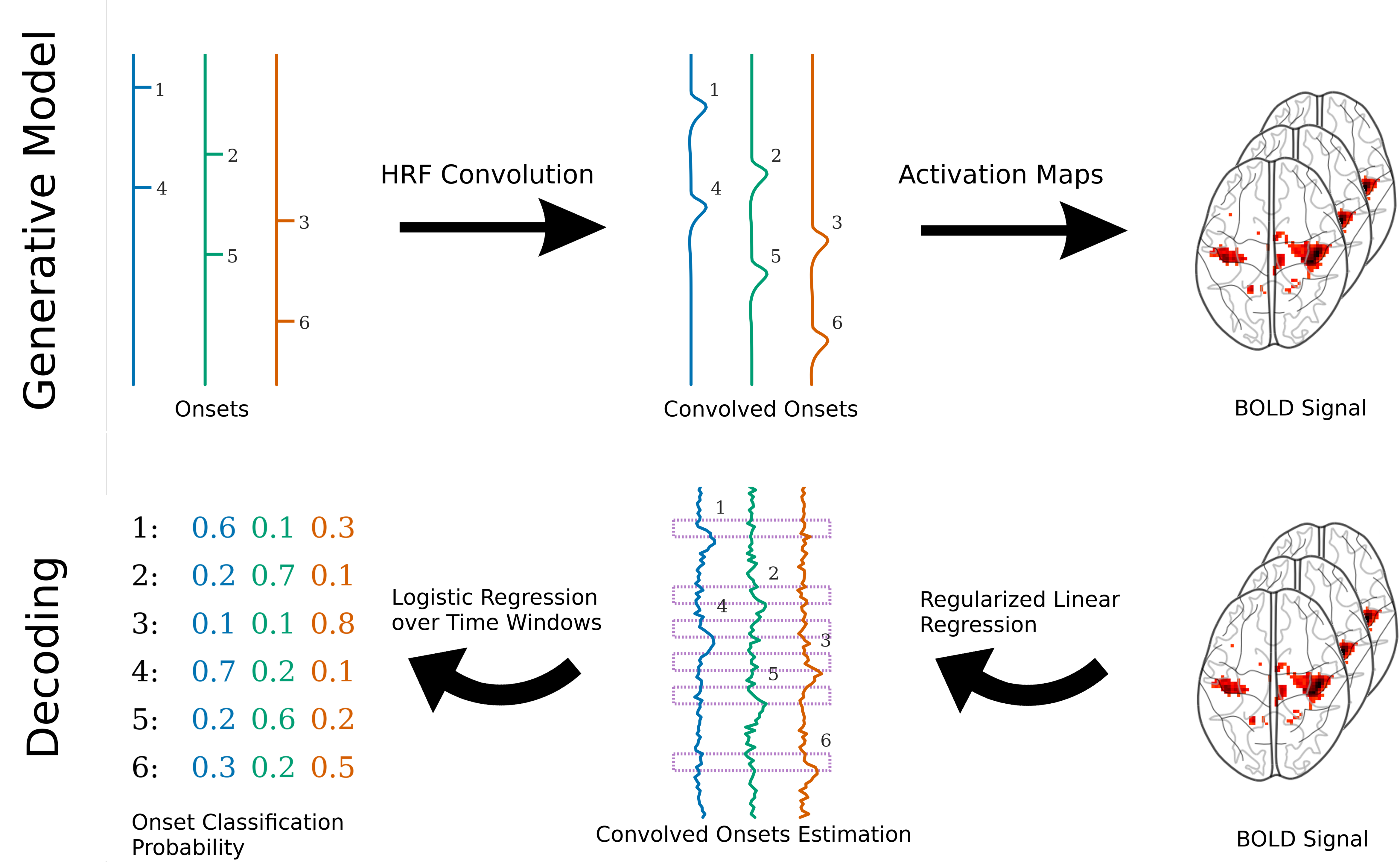
Most current functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) decoding analyses rely on statistical summaries of the data resulting from a deconvolution approach: each stimulation event is associated with a brain response. This standard approach leads to simple learning procedures, yet it is ill-suited for decoding events with short inter-stimulus intervals. In order to overcome this issue, we propose a novel framework that separates the spatial and temporal components of the prediction by decoding the fMRI time-series continuously, i.e. scan-by-scan. The stimulation events can then be identified through a deconvolution of the reconstructed time series. We show that this model performs as well as or better than standard approaches across several datasets, most notably in regimes with small inter-stimuli intervals (3 to 5s), while also offering predictions that are highly interpretable in the time domain. This opens the way toward analyzing datasets not normally thought of as suitable for decoding and makes it possible to run decoding on studies with reduced scan time.